前言
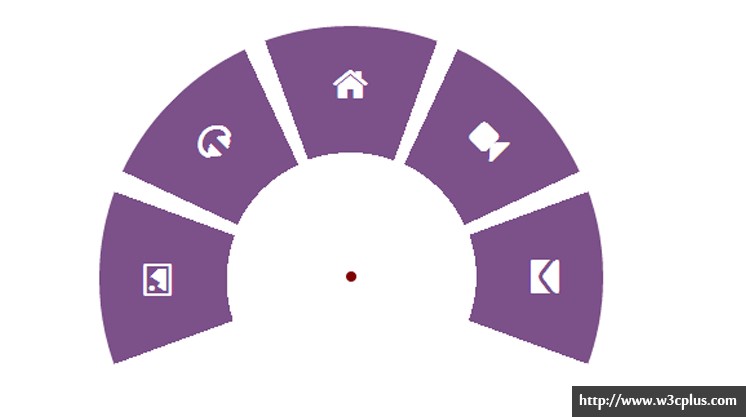
不知大家有没有注意本站的文章页,底部有个白色半圆文章小工具。如果觉得有兴趣学习制作方案,可以继续往下看。
在这个教程中,我会教你使用CSS变形制作圆形导航。 我会带你一步步地创建样式,讲解背后的数学知识和简单的逻辑,让你对这技术有清晰的认识。
正如我提到的,使用CSS变形创建样式,会用到相关的基础数学知识。但是不必担心, 用到的数学非常简单,我会带你一步步地客克服它。
我要指出原技术属于Ana Tudor。我把它修改成我想要效果,这也是我希望你的在教程结束时去做的:对这技术有深入而且清晰的认识,开始查阅资料并且构建自己的样式。
效果
demo:http://tympanus.net/Tutorials/CircularNavigation/
download:http://tympanus.net/Tutorials/CircularNavigation/CircularNavigation.zip
结构
我们要创建一个导航,因此我们会从常见的导航结构开始。我们需要一个div包含无序的项目列表, 一个开启和关闭导航栏的按钮,项目清单以及在第一个演示中导航栏打开时需要用到的额外的层。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
<button class="cn-button" id="cn-button">+</button> <div class="cn-wrapper" id="cn-wrapper"> <ul> <li><a href="#"><span class="icon-picture"></span></a></li> <li><a href="#"><span class="icon-headphones"></span></a></li> <li><a href="#"><span class="icon-home"></span></a></li> <li><a href="#"><span class="icon-facetime-video"></span></a></li> <li><a href="#"><span class="icon-envelope-alt"></span></a></li> </ul> </div> <div id="cn-overlay" class="cn-overlay"></div> |
ICONS”的制作来自于Font Awesome。
CSS变形中的数学知识
讲解数学的最佳方法是使用图形化解释而不是书面解释。所以我们会从逻辑开始并且在讲解过程中把数学知识应用进去,讲解结束之后,我们开始编码部分,那时你会准确地了解每条CSS语句的作用。
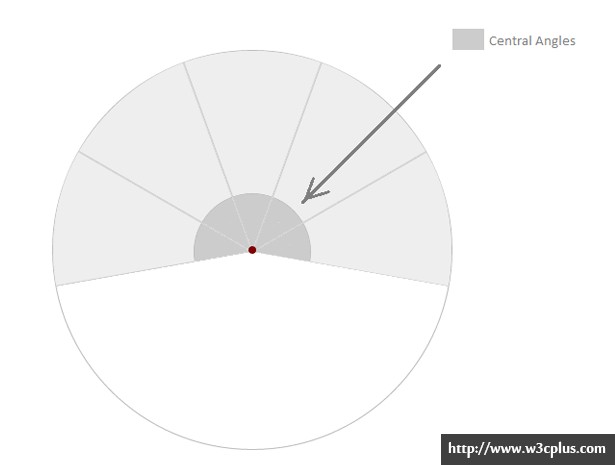
首先,让我们复习下什么是“圆心角”。这是带有简短解释的直观表示:
假如你想像例子一样要将所有的导航项分配到一个半圆中,在你的导航列表中有6项,那么每个角有一个圆心角:
|
1 |
180deg / 6 = 30deg |
如果你想要导航项占据整个圆,并且在这个圆中放入6个导航项,每一项的圆心角应该是:
|
1 |
360deg / 6 = 60deg |
这样你就可以计算你想要的圆心角,此后我们会将简单的数学应用到CSS变形中,真正意义上创建这些角。
为了创建期望的圆心角度的角,我们必须让导航项倾斜(用skew()CSS函数):
|
1 |
90deg-xdeg, /* x是你想得到的圆心角的值。*/ |
很简单。但是在这种情况下,列表项里的内容都会倾斜,而且内容看起来会变形,这些都不是我们想要的,所以为了内容正常显示,我们会“不倾斜”每个列表项的锚节点。
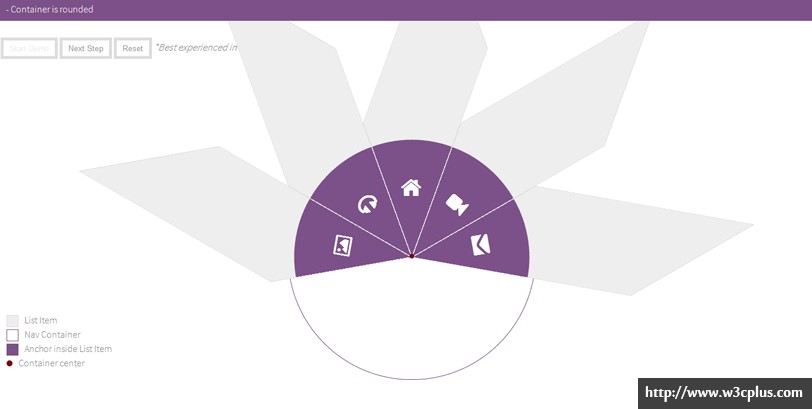
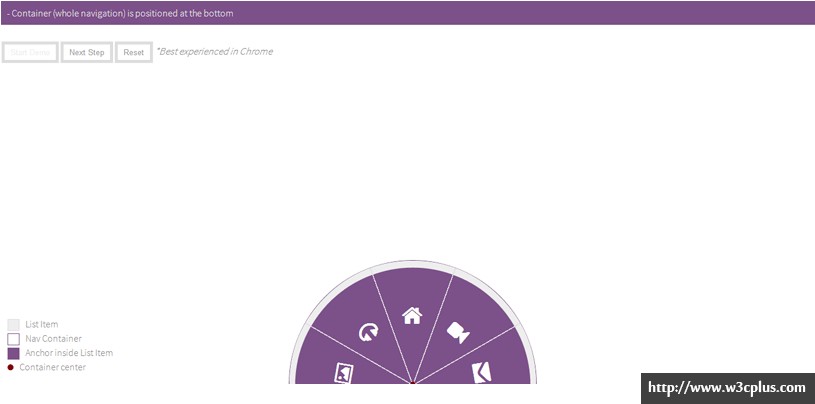
我构建了一个在线的交互式演示,它会展示变形是如何一步步地应用到导航项中,让你对代码要做的事情有清晰的了解。(注意演示中在步骤顺序稍微和教程中的不一样)。
在对我们接下来要做的事情有更清晰理解的时候,在你也许想要看到分布演示。我为演示加了一个预排功能,会解释每一步中的内容,所以花一分钟时间播放这演示,对我们将要做的有更深入的了解。 你可以使用Start Demo 按钮从头到尾播放演示,或者使用Next Step 按钮一步步地播放,并且可以使用Reset 按钮随时重置演示过程。
demo:http://tympanus.net/Tutorials/CircularNavigation/interactivedemo/index.html
以下是你将要在演示中看到的步骤截图:
初始状态
第一步
第二步
第三步
第四步
第五步
第六步
那么让我们来重温一下:
- 我们需要将导航项绝对定位在容器里面
- 将每一项的变换原点设置成他们的右下角
- 然后往左上角平移导航项,让它们的变换原点和容器中心相吻合
- 然后按照公式顺时针旋转每一项到指定的位置:对于第i项,需要旋转:
i*x,其中x是圆心角的值。 - 然后让它们变形以获取我们想要的圆心角(使用上面提到过的公式)。
在我们的例子中,我们有5个导航项,意味着5个圆心角,我们只想要圆的上半部分,那么根据上面解释的数学公式,每一项应该有36度圆心角,但是在我们的例子中,我把圆心角设为40度(因为这样可以提供更大的点击区域),那么所有圆心角的总和应该是5 * 40 = 200度,这大于180度。 在这种情况下,我们要做的仅仅是逆时针旋转(200-180)/2度确保两边相对称。
这时候我们已经创建了圆心角并且定位了元素。 但是倾斜列表项也造成了内容的倾斜, 如此一来内容会变形, 我们要在这里应用的最后一条数学规则会确保a标签不会变形而且内容可见。规则就是:
反向倾斜a标签,意味着按列表项需要按相反的值倾斜, 然后用- [90 – (x/2) ]的值反向 旋转,x是圆心角的值。那么对于40度的圆心角,我们需要倾斜a标签-40度并且按-[ 90 – (40/2) ] = -70 度旋转。
a标签被绝对定位在它们的父级中,而且列表项的overflow被设置为hidden,这意味着a标签的一部分被裁切,所以为了确保a标签中的文字/图标出现在可见部分,我们将内容居中对齐。
这就是我们在创建导航栏切割用到的所有数学知识!啊,终于结束了,对吧?
那么让我们再一次快速地回顾一下:
- 旋转导航项到指定位置:角度y = i * x (i是第几项,x是圆心角的值)
- 按照90-x倾斜(x是圆心角的值)
- 如果要相对称反方向旋转导航项(这一步实际上和前一步合并)
- “反向倾斜”“反向旋转”导航中的a标签(设置text-align为center)
当然,我们跳过了移动列表项使得转换原点和容器中心保持一致的步骤。以上是创建角的所有东西,但是并不是创建整个导航栏所需要的。一个简单的步骤被保留着,那就是常规的样式编写,那么让我们开始写CSS,在讲解过程中谈谈这些步骤。
CSS
我们先写第一个演示的样式。
将Modernizr类应用到body标签,标示浏览器是否支持,为不支持CSS变形的旧浏览器提供一个非常简单和基础的备用样式。
我们从编写导航容器开始。它会相对窗口定位在页面底部的中间,最初会被按比例缩小,点击展开按钮时,它会打开/按比例放大。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
.csstransforms .cn-wrapper { font-size:1em; width: 26em; height: 26em; overflow: hidden; position: fixed; z-index: 10; bottom: -13em; left: 50%; border-radius: 50%; margin-left: -13em; transform: scale(0.1); transition: all .3s ease; } /* class applied to the container via JavaScript that will scale the navigation up */ .csstransforms .opened-nav { border-radius: 50%; transform: scale(1); } |
我们也需要给触发导航栏打开和闭合的按钮写样式并且定位它。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
.cn-button { border:none; background:none; color: white; text-align: Center; font-size: 1.5em; padding-bottom: 1em; height: 3.5em; width: 3.5em; background-color: #111; position: fixed; left: 50%; margin-left: -1.75em; bottom: -1.75em; border-radius: 50%; cursor: pointer; z-index: 11 } .cn-button:hover, .cn-button:active, .cn-button:focus{ background-color: #222; } |
当导航栏打开时,一个层会覆盖在页面上。这是覆盖层的样式:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
.cn-overlay{ width:100% height:100%; background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.6); position:fixed; top:0; left:0; bottom:0; right:0; opacity:0; transition: all .3s ease; z-index:2; pointer-events:none; } /* Class added to the overlay via JavaScript to show it when navigation is open */ .cn-overlay.on-overlay{ pointer-events:auto; opacity:1; } |
现在我们为导航项和它们的a标签编写样式,应用之前解释过的逻辑和基于数学的变形。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 |
.csstransforms .cn-wrapper li { position: absolute; font-size: 1.5em; width: 10em; height: 10em; transform-origin: 100% 100%; overflow: hidden; left: 50%; top: 50%; margin-top: -1.3em; margin-left: -10em; transition: border .3s ease; } .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a { display: block; font-size: 1.18em; height: 14.5em; width: 14.5em; position: absolute; bottom: -7.25em; right: -7.25em; border-radius: 50%; text-decoration: none; color: #fff; padding-top: 1.8em; text-align: center; transform: skew(-50deg) rotate(-70deg) scale(1); transition: opacity 0.3s, color 0.3s; } .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a span { font-size: 1.1em; opacity: 0.7; } /* for a central angle x, the list items must be skewed by 90-x degrees in our case x=40deg so skew angle is 50deg items should be rotated by x, minus (sum of angles - 180)2s (for this demo) */ .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li:first-child { transform: rotate(-10deg) skew(50deg); } .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li:nth-child(2) { transform: rotate(30deg) skew(50deg); } .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li:nth-child(3) { transform: rotate(70deg) skew(50deg) } .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li:nth-child(4) { transform: rotate(110deg) skew(50deg); } .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li:nth-child(5) { transform: rotate(150deg) skew(50deg); } .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li:nth-child(odd) a { background-color: #a11313; background-color: hsla(0, 88%, 63%, 1); } .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li:nth-child(even) a { background-color: #a61414; background-color: hsla(0, 88%, 65%, 1); } /* active style */ .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li.active a { background-color: #b31515; background-color: hsla(0, 88%, 70%, 1); } /* hover style */ .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li:not(.active) a:hover, .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li:not(.active) a:active, .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li:not(.active) a:focus { background-color: #b31515; background-color: hsla(0, 88%, 70%, 1); } |
我们会为不支持CSS变形的浏览器提供简单、基本的备用样式。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 |
.no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper{ font-size:1em; height:5em; width:25.15em; bottom:0; margin-left: -12.5em; overflow: hidden; position: fixed; z-index: 10; left:50%; border:1px solid #ddd; } .no-csstransforms .cn-button{ display:none; } .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper li{ position:static; float:left; font-size:1em; height:5em; width:5em; background-color: #eee; text-align:center; line-height:5em; } .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a{ display:block; width:100%; height:100%; text-decoration:none; color:inherit; font-size:1.3em; border-right: 1px solid #ddd; } .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a:last-child{ border:none; } .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a:hover, .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a:active, .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a:focus{ background-color: white; } .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper li.active a { background-color: #6F325C; color: #fff; } |
当然我们想要我们的导航可响应,所以导航会收缩到合适更小的屏幕。这是圆形导航和简单情况的响应式样式。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
@media screen and (max-width:480px){ .csstransforms .cn-wrapper{ font-size:.68em; } .cn-button{ font-size:1em; } .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li { font-size:1.52em; } } @media screen and (max-width:320px){ .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper{ width:15.15px; margin-left: -7.5em; } .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper li{ height:3em; width:3em; } } |
那是第一个演示!我们继续下一个演示。
第二个圆形样式和第一个不一样,但是除了三处不同,所有用来创建这种风格的导航的数学知识、逻辑、变形和前一个很像。所以我们不会再去回顾相同的解释, 只会涉及这种风格的三个不同的步骤。
再一次引用上面的例子,只改变一点点简单的CSS规则,看看导航项的形状发生的变化。
我们给带有透明背景色的a标签使用线性渐变的背景色。结果看起会是这样:
你可以从这里看到我们前进的方向。接下来,我们会稍微改变每一个导航项的旋转角度增加它们之间的距离。我们也要移出列表项的和容器的背景色、边框,以及减少a标签顶部填充距离将图标往上靠到垂直居中的位置。得到的效果像是这样:
正如你看到的,导航已经开始看起来不一样了;我们已经完成了一大半了。
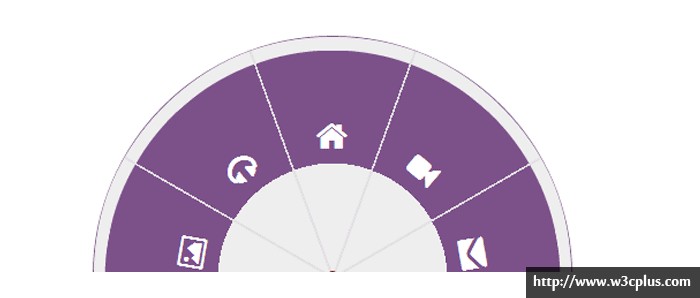
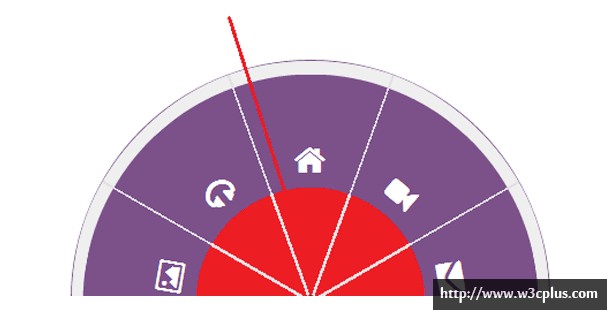
我们仍然有很重的事情要做。根据目前的情况,a标签的点击区域依旧比我们想要的大。我们想要的是只有图片中显示的带颜色的部分的导航栏是可以点击的。 下面的图片准确地显示a标签的可点击区域。
当你移到图片中的红色区域,a标签的下面部分,a标签的悬浮状态会被触发,这是不正常的事情,因为我们想要的a标签只是紫色区域,我们需要防止鼠标在a标签的下半部分被触发。为了达到目的,我们会在圆形容器的上面放一个“cover”,它是圆形的,会覆盖a标签的下半部分,因此阻止这些部分的鼠标事件。为了避免添加额外的空标签我们会使用伪元素。
因此,应用这三个步骤,我们的CSS,改变整体样式(颜色和大小)的导航,导航项看起来像预览上图,我们最终得到以下CSS:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 |
.csstransforms .cn-wrapper { position: absolute; top: 100%; left: 50%; z-index: 10; margin-top: -13em; margin-left: -13.5em; width: 27em; height: 27em; border-radius: 50%; background: transparent; opacity: 0; transition: all .3s ease 0.3s; transform: scale(0.1); pointer-events: none; overflow: hidden; } /*cover to prevent extra space of anchors from being clickable*/ .csstransforms .cn-wrapper:after{ color: transparent; content:"."; display:block; font-size:2em; width:6.2em; height:6.2em; position: absolute; left: 50%; margin-left: -3.1em; top:50%; margin-top: -3.1em; border-radius: 50%; z-index:10; } .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li { position: absolute; top: 50%; left: 50%; overflow: hidden; margin-top: -1.3em; margin-left: -10em; width: 10em; height: 10em; font-size: 1.5em; transition: all .3s ease; transform: rotate(76deg) skew(60deg); transform-origin: 100% 100%; pointer-events: none; } .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a { position: absolute; right: -7.25em; bottom: -7.25em; display: block; width: 14.5em; height: 14.5em; border-radius: 50%; background: #429a67; background: radial-gradient(transparent 35%, #429a67 35%); color: #fff; text-align: center; text-decoration: none; font-size: 1.2em; line-height: 2; transition: all .3s ease; transform: skew(-60deg) rotate(-75deg) scale(1); pointer-events: auto; } .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a span { position: relative; top: 1.8em; display: block; font-size: .5em; font-weight: 700; text-transform: uppercase; } .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a:hover, .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a:active, .csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a:focus { background: radial-gradient(transparent 35%, #449e6a 35%); } |
导航栏展开的时候,我们想要第二个演示中的导航项以扇形效果展开。
为了达到这种效果,我们要将所有导航项定位到同一个位置和角度/倾斜度:
|
1 |
rotate(76deg) skew(60deg). |
使用过度延迟使得导航项能在容器放大后展开。当导航关闭的时候,我们会在容器缩小之前等待导航项缩到一起。
当展开按钮被点击,我们会通过旋转每一项到圆里面的最终位置展开导航项。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
.csstransforms .opened-nav { border-radius: 50%; opacity: 1; transition: all .3s ease; transform: scale(1); pointer-events: auto; } .csstransforms .opened-nav li { transition: all .3s ease .3s; } .csstransforms .opened-nav li:first-child { transform: rotate(-20deg) skew(60deg); } .csstransforms .opened-nav li:nth-child(2) { transform: rotate(12deg) skew(60deg); } .csstransforms .opened-nav li:nth-child(3) { transform: rotate(44deg) skew(60deg); } .csstransforms .opened-nav li:nth-child(4) { transform: rotate(76deg) skew(60deg); } .csstransforms .opened-nav li:nth-child(5) { transform: rotate(108deg) skew(60deg); } .csstransforms .opened-nav li:nth-child(6) { transform: rotate(140deg) skew(60deg); } .csstransforms .opened-nav li:nth-child(7) { transform: rotate(172deg) skew(60deg); } |
当然, 我们会为不支持的浏览器提供基本的备用样式。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
.no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper ul{ display:inline-block; } .no-csstransforms li{ font-size:1em; width:5em; height:5em; float:left; line-height:5em; text-align:center; background-color: #fff; } .no-csstransforms li a{ display:block; height:100%; width:100%; text-decoration: none; color: inherit; } .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a:hover, .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a:active, .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper li a:focus{ background-color: #f8f8f8; } .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper li.active a { background-color: #6F325C; color: #fff; } .no-csstransforms .cn-button{ display:none; } |
而且,导航也要是响应式的,因此我们会在小屏幕中缩小它。这里是圆形导航和简单情况的响应式样式。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
@media only screen and (max-width: 620px) { .no-csstransforms li{ width:4em; height:4em; line-height:4em; } } @media only screen and (max-width: 500px) { .no-ccstransforms .cn-wrapper{ padding:.5em; } .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper li{ font-size:.9em; width:4em; height:4em; line-height:4em; } } @media only screen and (max-width: 480px) { .csstransforms .cn-wrapper{ font-size: .68em; } .cn-button{ font-size:1em; } } @media only screen and (max-width:420px){ .no-csstransforms .cn-wrapper li{ width:100%; height:3em; line-height:3em; } } |
这是你创建这种风格需要用到的几乎所有的样式。
Javasctrip
我们不会为这些演示使用任何框架。 我会使用David De Sandro的Classie.js 添加或者移出class。并且最终对于不支持addEventListener和removeEventListener的浏览器,我们会使用 Jonathan Neal 的 EventListener polyfill。
我们为两个演示中的按钮添加事件监听。点击按钮或者聚焦到上面都会触发导航栏开启/关闭。
对于第一个演示,当导航栏展开的时候点击导航栏外面的任何地方都会使它关闭。让我们从第一个演示的JavaScript开始。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
(function(){ var button = document.getElementById('cn-button'), wrapper = document.getElementById('cn-wrapper'), overlay = document.getElementById('cn-overlay'); //open and close menu when the button is clicked var open = false; button.addEventListener('click', handler, false); button.addEventListener('focus', handler, false); wrapper.addEventListener('click', cnhandle, false); function cnhandle(e){ e.stopPropagation(); } function handler(e){ if (!e) var e = window.event; e.stopPropagation();//so that it doesn't trigger click event on document if(!open){ openNav(); } else{ closeNav(); } } function openNav(){ open = true; button.innerHTML = "-"; classie.add(overlay, 'on-overlay'); classie.add(wrapper, 'opened-nav'); } function closeNav(){ open = false; button.innerHTML = "+"; classie.remove(overlay, 'on-overlay'); classie.remove(wrapper, 'opened-nav'); } document.addEventListener('click', closeNav); })(); |
第二个演示的JavaScript和前一个很像,除了为这个案例定制的部分:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
(function(){ var button = document.getElementById('cn-button'), wrapper = document.getElementById('cn-wrapper'); //open and close menu when the button is clicked var open = false; button.addEventListener('click', handler, false); button.addEventListener('focus', handler, false); function handler(){ if(!open){ this.innerHTML = "Close"; classie.add(wrapper, 'opened-nav'); } else{ this.innerHTML = "Menu"; classie.remove(wrapper, 'opened-nav'); } open = !open; } function closeWrapper(){ classie.remove(wrapper, 'opened-nav'); } })(); |
这就是我要说的!我希望你喜欢这个教程并且发现它的价值所在!
效果
demo:http://tympanus.net/Tutorials/CircularNavigation/
download:http://tympanus.net/Tutorials/CircularNavigation/CircularNavigation.zip
如需转载烦请注明出处:
英文原文:http://tympanus.net/codrops/2013/08/09/building-a-circular-navigation-with-css-transforms
中文译文:http://www.w3cplus.com/css3/building-a-circular-navigation-with-css-transforms.html












学习了
nice,很好
介绍的太长了,这果断是外国大神写的啊
群主,网站的效果很酷,很有新意
谢谢
要多多学习才行了